M. Mariani, A. Basso Peressut, S. Latorrata, R. Balzarotti, M. Sansotera, G. Dotelli
Energies, 14(24) (2021), 8387
https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/14/24/8387
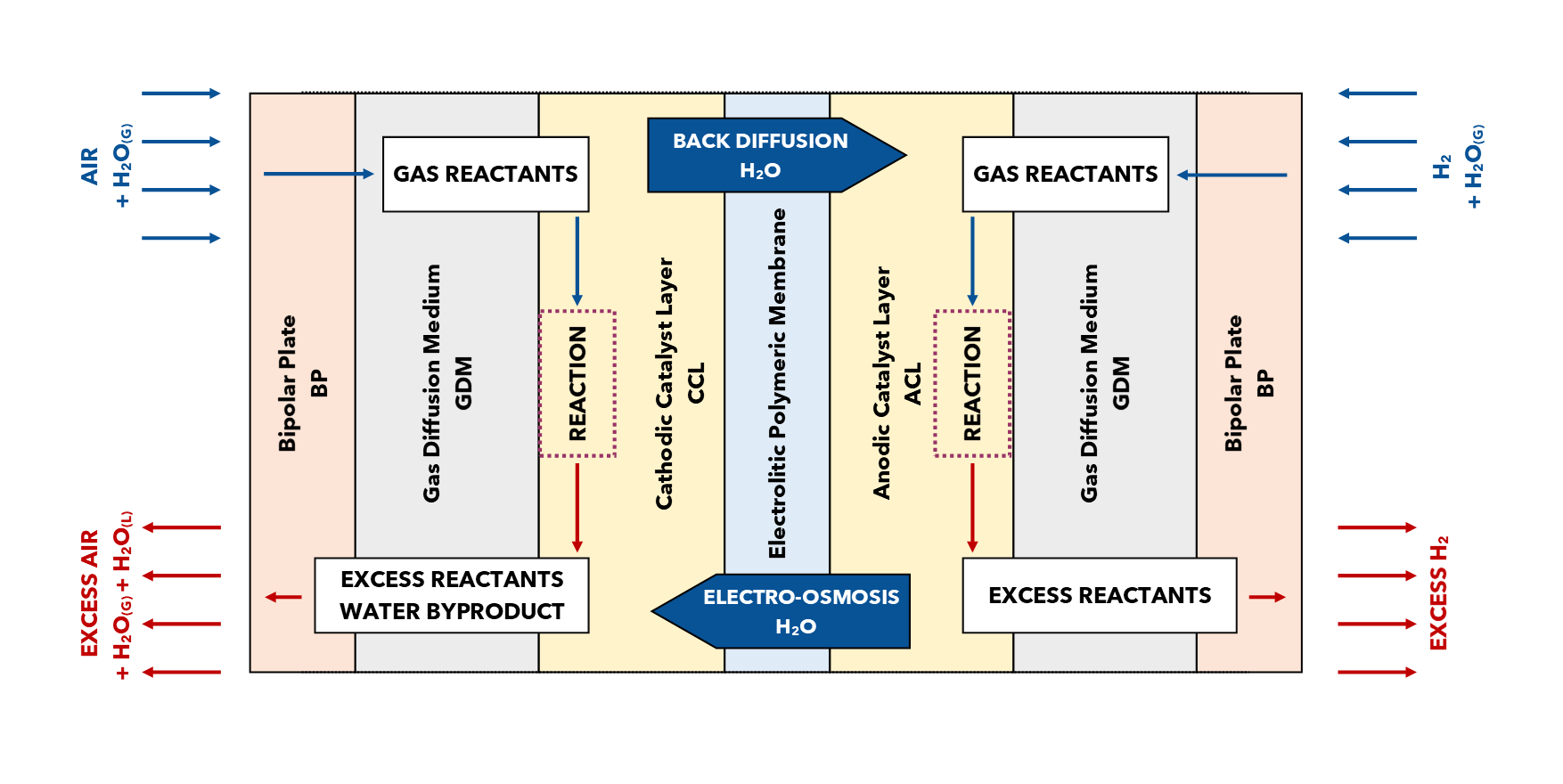
This work presents a comprehensive review of the state of the art of the use of fluorinated polymers for the hydrophobization of gas diffusion media (GDM) of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Fluorine-based polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), the most common ones, as well as other compounds such as PFA, PVDF, PFPE, and CF4, are introduced in the GDM as hydrophobic agents, with the aim of improving the water management of the fuel cell. In fact, membrane dehydration and cell flooding are typical issues faced by PEM fuel cells at their operating conditions, and their avoidance is strictly related to the employment of fluorinated materials in both gas diffusion layer (GDL) and microporous layer (MPL). This review paper describes in detail the effect of the use of these materials on the performance of the device under several operating conditions, focusing on the influence of different polymer amounts on the variation of properties such as conductivity, hydrophobicity, porosity, and durability.